If you are a truck driver or a carrier, you need to be aware of the DOT (Department of Transportation) regulations and violations. The DOT is the federal agency that oversees the safety and compliance of commercial vehicles and drivers. The DOT has many rules and standards that apply to different aspects of trucking, such as hours of service, licensing, drug and alcohol testing, vehicle inspection, maintenance, and hazardous materials. Failing to follow these rules can result in DOT violations, which can have serious consequences for your business and reputation.
MOST COMMON DOT VIOLATIONS
DOT violations can result in serious consequences, including fines, loss of driving privileges, and even criminal charges in some cases. Below are some of the most common and important DOT violations that cannot be ignored in the first place.
Before listing the violations, it is important to understand that DOT violations affect drivers, vehicles, records, and safety-sensitive employees, and are monitored by the FMCSA.
HOURS OF SERVICE (HOS) VIOLATIONS
CDL drivers are required to follow strict HOS regulations to prevent accidents caused by driver fatigue.
Common HOS Violations Include:
- Driving beyond the maximum number of hours allowed
- Failing to take required breaks or rest periods
- Falsifying logbooks or electronic logging devices
- Not maintaining proper ELD records
Why it matters: HOS violations are one of the most frequently cited violations in DOT inspections and can directly impact CSA scores and FMCSA safety ratings.

VEHICLE MAINTENANCE VIOLATIONS
DOT-compliant CDL drivers are required to undergo regular inspections and maintenance to ensure they are safe to operate on the road.
Common Maintenance Violations Include:
- Failure to perform required inspections
- Failure to repair defects identified during inspections
- Operating vehicles with unsafe or defective equipment
- Failure to maintain accurate maintenance records
Why it matters: Poor vehicle maintenance can lead to roadside inspection failures, out-of-service orders, and heavy fines.
DRIVER QUALIFICATION VIOLATIONS
Truck drivers must meet certain qualifications and undergo specific training before operating a commercial vehicle.
Common Qualification Violations Include:
- Operating a vehicle without a valid commercial driver's license (CDL)
- Driving with a suspended or revoked license
- Failing to meet other driver qualification requirements
- Missing required medical certificates or DQ file documents
Why it matters: Incomplete driver qualification files can cause carriers to fail FMCSA audits and increase liability.
EQUIPMENT VIOLATIONS
FMCSA-regulated vehicles must be equipped with certain safety features, including proper lighting, reflectors, brakes, tires, and emergency equipment.
Common Equipment Violations Include:
- Operating a vehicle with non-functioning or defective equipment
- Failing to properly secure cargo
- Missing emergency triangles or safety equipment
- Broken or missing lights, reflectors, or mirrors
Why it matters: Equipment violations affect vehicle safety scores and are a common cause of out-of-service orders during inspections.
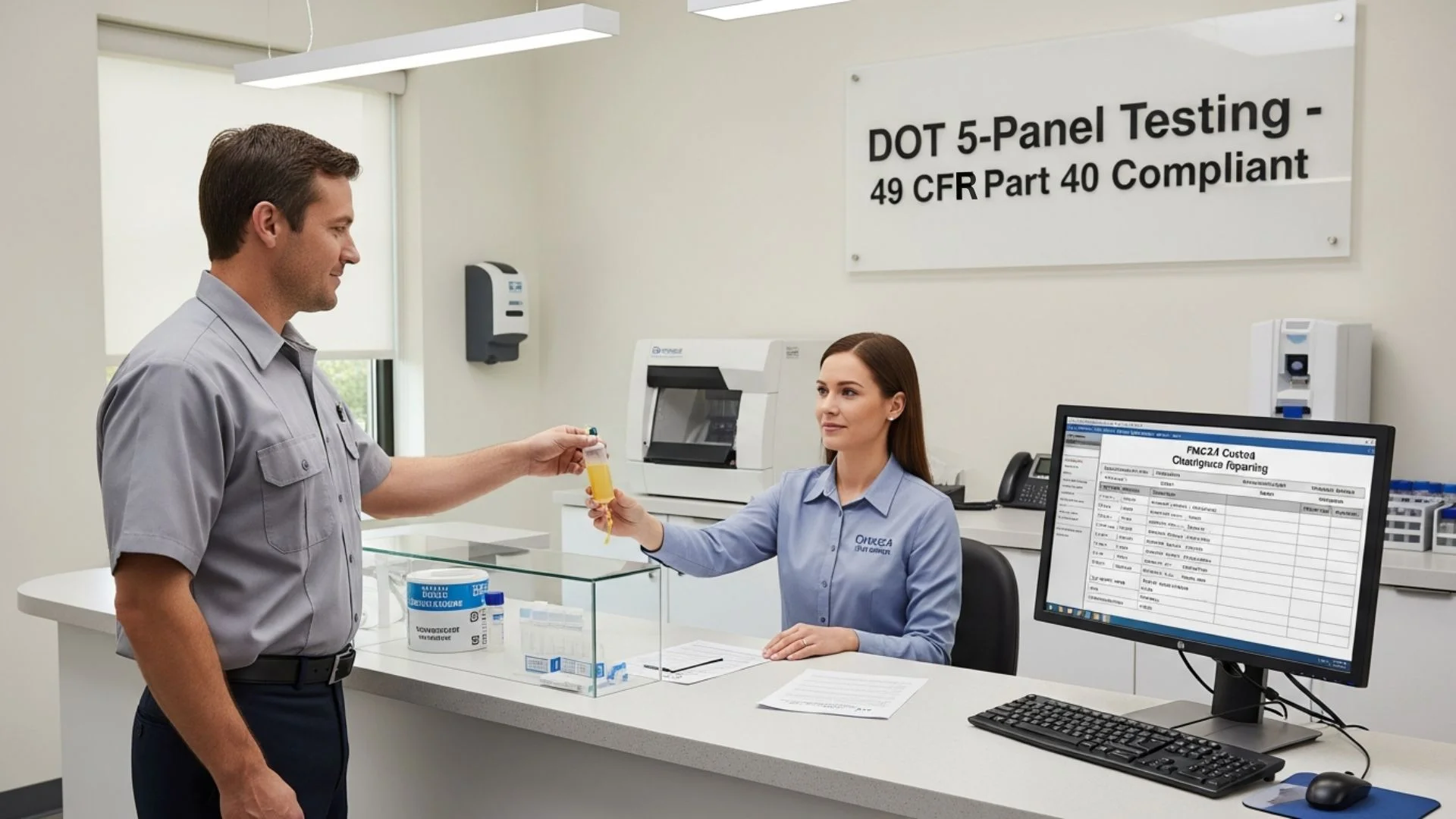
DOT DRUG & ALCOHOL TESTING VIOLATIONS
Safety-sensitive employees, including CDL holders, pilots, and railroad employees, truck drivers are required to undergo DOT drug and alcohol testing.
Common Drug & Alcohol Violations Include:
- Failing a drug or alcohol test
- Refusing to take a test
- Violating any provision of DOT drug and alcohol testing regulations
- Not being enrolled in a DOT Consortium (C/TPA)
- Missing random drug testing requirements
- Ignoring return-to-duty procedures
Why it matters: Drug testing ensures employees are not under the influence while performing duties and protects the public and carriers from accidents and liabilities.
Suggested:
DOT Rules and Regulations You Can't Afford to Ignore
How to Prepare for FMCSA Safety Audit?
DOT VIOLATIONS CONSEQUENCES
DOT violations can have serious consequences, ranging from fines and penalties to suspension of driving privileges and even criminal charges. By:
- Maintaining proper vehicle maintenance
- Adhering to Hours of Service regulations
- Completing driver qualification files
- Avoiding drug and alcohol violations
Companies can contribute to a safer and more secure transportation system while staying fully DOT and FMCSA compliant.
Stay Compliant with goMDnow Services
Are you an employer of commercial motor vehicle drivers looking for a reliable and convenient solution for DOT-mandated drug and alcohol testing?
Look no further than goMDnow's DOT/ Non-DOT Drug Testing! Our comprehensive service provides access to a nationwide network of testing facilities, flexible scheduling, and electronic reporting to help you stay compliant with DOT regulations and promote safety on the road.







